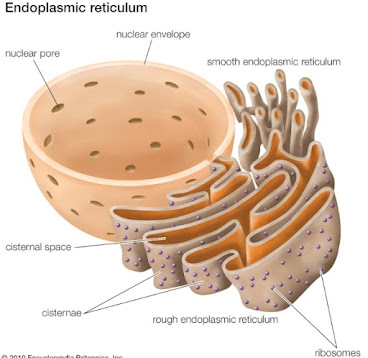
The export of proteins and lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a crucial process in eukaryotic cells, facilitating the transport of these biomolecules to various cellular destinations. This process primarily occurs through a structured pathway known as the secretory pathway, which includes several key organelles and mechanisms.
Secretory Pathway
The secretory pathway for proteins and lipids follows a defined route:
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER): Proteins destined for secretion are synthesized on ribosomes attached to the RER. These ribosomes are directed to the ER by a signal sequence in the nascent polypeptide chain, allowing for co-translational translocation into the ER lumen where proteins begin to fold and undergo modifications.
- Golgi Apparatus: After synthesis, proteins and lipids are packaged into transport vesicles that bud off from the ER and travel to the Golgi apparatus. Here, they undergo further processing, including glycosylation and sorting based on their final destinations.
- Secretory Vesicles: Processed proteins and lipids are then packaged into secretory vesicles that transport them to the plasma membrane or other organelles. Upon reaching their destination, these vesicles fuse with the membrane, releasing their contents outside the cell or delivering them to specific intracellular locations.

Image source: Life Sciences, Fundamental & Practices-I by P. Kumar & U. Mina, (2016)
Mechanisms of Export
Vesicular Transport
- COPII Vesicles: These vesicles are specifically involved in transporting proteins from the ER to the Golgi apparatus. The coat protein complex II (COPII) facilitates the budding of vesicles from the ER membrane, ensuring that only correctly folded and assembled proteins are included in these transport vehicles.
- Lipid Transfer: Lipids can also be exported via vesicles or through non-vesicular mechanisms involving lipid transfer proteins that facilitate lipid movement between membranes without forming vesicles. This is essential for maintaining lipid homeostasis within cells.
Non-Vesicular Transport
In addition to vesicular mechanisms, there are non-vesicular pathways where lipids can be transferred directly between membranes through specialized proteins. These include:- Lipid Transfer Proteins (LTPs): These proteins can shuttle lipids between different membrane compartments, playing a crucial role in lipid metabolism and distribution within cells.