The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is a type of endoplasmic reticulum characterized by the absence of ribosomes on its surface, giving it a smooth appearance. It is a network of tubular membranes and vesicles that extends throughout the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. The SER plays a crucial role in various cellular processes, particularly in lipid synthesis and metabolism.
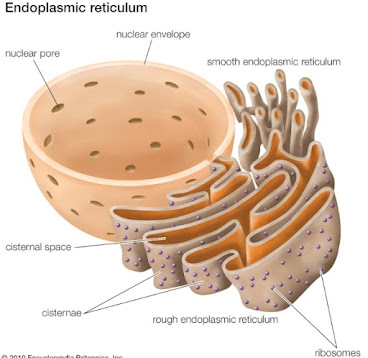 |
| Structure of smooth endoplasmic reticulum |
Functions of the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Lipid Synthesis:
- The SER is primarily involved in the synthesis of lipids, including phospholipids and cholesterol, which are essential components of cellular membranes. Phospholipids are critical for forming the lipid bilayer of cell membranes, while cholesterol contributes to membrane fluidity and stability.
- Steroid Hormone Production:
- In specialized cells, such as those in the adrenal glands and gonads, the SER is responsible for synthesizing steroid hormones from cholesterol. This includes hormones like cortisol, aldosterone, and sex hormones (estrogen and testosterone) that regulate various physiological processes.
- Detoxification:
- The smooth ER plays a significant role in detoxifying harmful metabolic byproducts and drugs. In liver cells, enzymes within the SER convert these substances into water-soluble compounds that can be easily excreted from the body.
- Carbohydrate Metabolism:
- The SER is involved in carbohydrate metabolism, including the conversion of glycogen to glucose. The enzyme glucose-6-phosphatase, found in the SER, catalyzes this conversion, which is vital for maintaining blood sugar levels.
- Calcium Ion Storage:
- In muscle cells, a specialized form of the SER known as the sarcoplasmic reticulum regulates calcium ion concentrations. It stores calcium ions and releases them during muscle contraction, thereby playing a critical role in muscle function.
Mechanism of Lipid Synthesis in Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
The lipid synthesis process in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum involves several key steps:- Fatty Acid Synthesis:
- Fatty acids are synthesized from acetyl-CoA through a series of enzymatic reactions. These fatty acids can then be further modified or elongated to form various lipid molecules.
- Phospholipid Synthesis:
- Phospholipids are synthesized on the cytosolic side of the SER membrane. Enzymes catalyze reactions between fatty acids and water-soluble precursors (e.g., CDP-choline) to produce phospholipids, which are then incorporated into cellular membranes.
- Cholesterol Synthesis:
- Cholesterol is synthesized from acetyl-CoA through a multi-step process involving several intermediates. Enzymes located in the SER facilitate these reactions, ultimately leading to cholesterol production.
- Transport to Other Organelles:
- Once synthesized, lipids are transported from the smooth ER to other cellular compartments such as the Golgi apparatus or directly integrated into cellular membranes via vesicular transport mechanisms.
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is an essential organelle involved in lipid synthesis and metabolism, detoxification processes, carbohydrate metabolism, and calcium storage. Its functions are critical for maintaining cellular homeostasis and supporting various physiological processes within eukaryotic cells. Understanding the role of SER in lipid synthesis provides insights into how cells manage their lipid content and respond to metabolic demands.

No comments:
Post a Comment